Biology in the Laboratory
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Activity
Investigating the effect of temperature and pH on enzyme activity
Introduction
Write an introduction of about 200 words considering the following questions. You can take help from the textbook, practical manual, class lectures, or the internet while answering these questions. (Do not write questions in the notebook. Only write the answers as paragraphs.)
- What are enzymes?
- How is the structure of enzymes maintained?
- How do enzymes increase the rate of chemical reactions?
- What are the factors that can affect the rate of chemical reactions?
Materials and Methods
The following items are required for this experiment:
- Potato
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Vinegar or HCl
- Solution (1% w/v) of Sodium hydroxide or Potassium hydroxide or baking soda
- Boiling water bath
- Ice water bath
- Knife
- Test tubes and rack
- Permanent marker
- Glass Pipette
Follow these steps and record your observation in the laboratory manual:
- Peel and cut the potato into small pieces of equal sizes. Take six (6) test tubes and place a piece of potato in each test tube.
- Add one mL of water to one of the test tubes. Label this test tube as C.
- Label one test tube as B and place it in a boiling water bath for fifteen minutes. After fifteen minutes, add one mL of hydrogen peroxide and observe carefully if bubbles form in the test tube.
- Place one test tube in an ice water bath for fifteen minutes. Label this test tube as I. In another test tube, pour one mL of hydrogen peroxide and place it in an ice water bath. After fifteen minutes, pour the cold hydrogen peroxide into test tube I. Observe if any bubbles form.
- Label a test tube as H, and add 1 mL of hydrochloric acid to it. Add 1 mL of hydrogen peroxide and observe any bubbles.
- Label a test tube as N and add 1 mL of sodium hydroxide solution to it. Add 1mL of hydrogen peroxide solution to it. Observe if any bubbles form in it.
- Label a test tube as P and add 1mL of distilled water to it. Add 1mL of hydrogen peroxide and observe the bubbles formed in it.
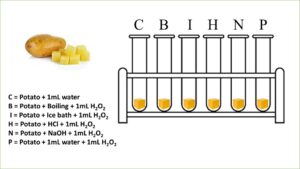
Results
Compare the bubbles formed in each test tube in the table below.
| Test Tube | C | B | I | H | N | P |
| Contents | Potato + 1mL water | Potato + Boiling + 1mL H2O2 | Potato + Ice bath + 1mL H2O2 | Potato + Acid + 1mL H2O2 | Potato + Base + 1mL H2O2 | Potato + 1mL water + 1mL H2O2 |
| Observation |
|
Discussion
Discuss the results while keeping in mind the following questions (in about 300-400 words). You can take help from the textbook, practical manual, class lectures, or the internet while answering these questions. (Do not write questions in the notebook. Only write the answers as paragraphs.)
- What does hydrogen peroxide form upon its breakdown?
- Which enzyme catalyzes the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide?
- Where can this enzyme be found other than potatoes?
- Why did no bubbles form in test tube C?
- Why did no bubbles form in test tube B?
- Compare the bubbles in test tubes I and P. Which tube has more bubbles? Why?
- Compare the bubbles in test tubes H, N, and P. Which tube has more bubbles? Why?
- Which of these tubes is positive control?
- Which of these tubes is negative control?